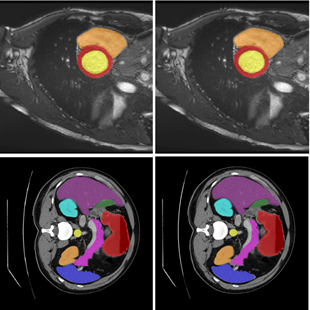
Summary: One of the familiar and promising deep learning approaches used for medical image segmentation is transformers, as they can capture long-range dependencies among the pixels by utilizing self-attention. Despite being successful in medical image segmentation, transformers need help in capturing local contexts of pixels in multimodal dimensions. Hence, we are developing lightweight transformers with memory-enabled decoders and attention-mixing decoders for precise medical image segmentation. Github
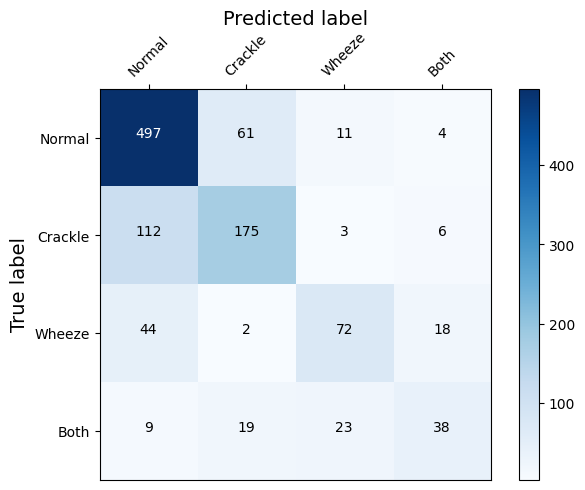
Summary: Early diagnosis, treatment, and regular monitoring can limit respiratory disease spread and adverse effects. However, more trained physicians are needed to ensure early diagnosis and treatment. This can be overcome by automating auscultation to identify anomalies like crackles, wheezes, and both. In this work, we propose a hybrid deep learning model combining ResNet34, a CNN model, a feature extractor, and Long Sort-term Memory (LSTM) as a predictor. We have also added an attention layer in the feature extractor to make the model learn the critical regions of the feature vector. Our model outperforms the recent state-of-the-art models and improves the performance of 2-class- and 4-class anomaly predictions. Github
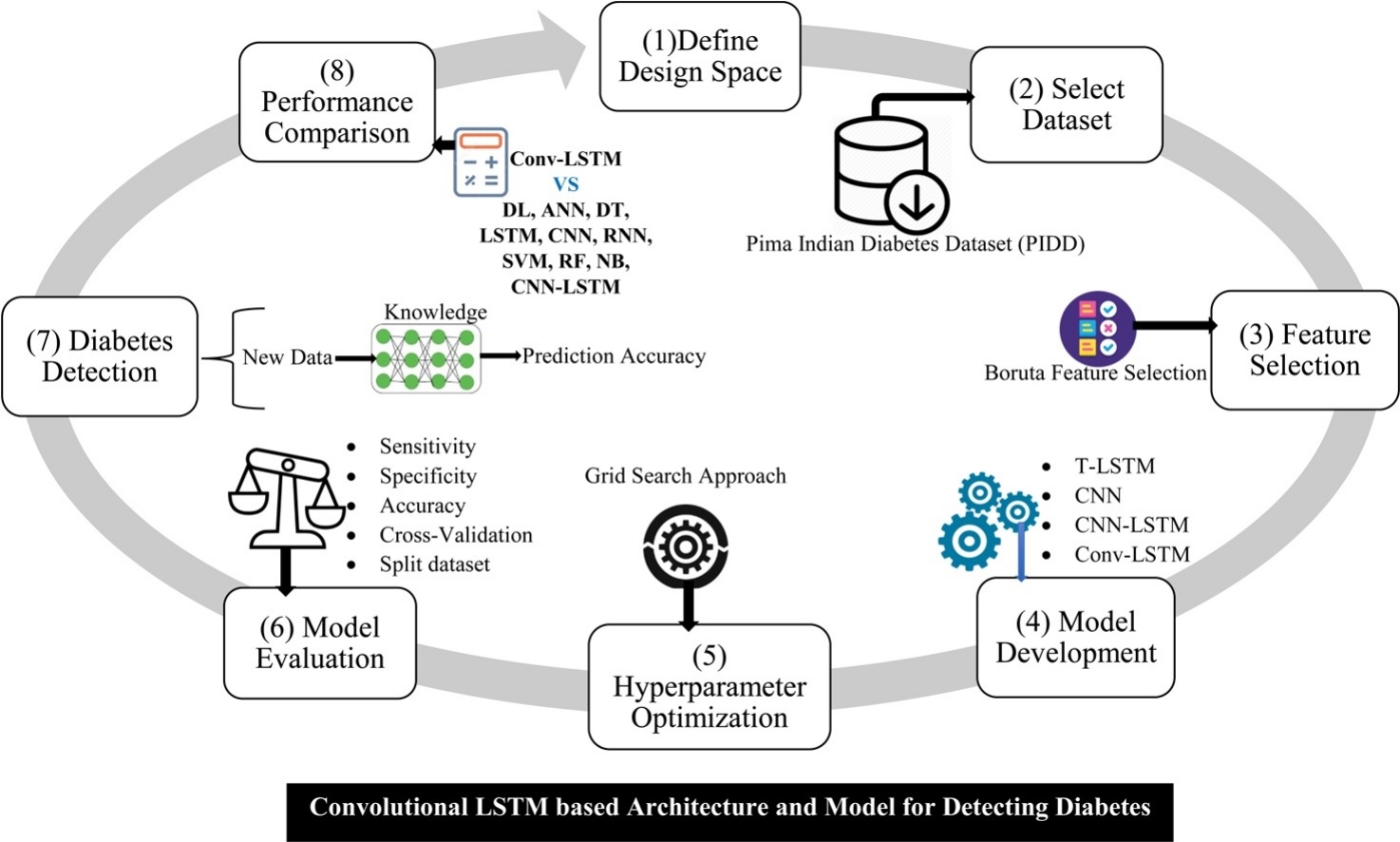
Summary: We developed a novel diabetes classifying model based on Convolutional Long Short-term Memory (Conv-LSTM) that was not applied yet in this regard. We applied another three popular models such as Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Traditional LSTM (T-LSTM), and CNN-LSTM and compared the performance with our developed model over the Pima Indians Diabetes Database (PIDD). Significant features were extracted from the dataset using Boruta algorithm that returned glucose, BMI, insulin, blood pressure, and age as important features for classifying diabetes patients more accurately. Initial experiment by splitting the dataset into separate training and testing sets, the Conv-LSTM-based model classified the diabetes patients with the highest accuracy of 91.38 %. In later, using cross-validation technique the Conv-LSTM model achieved the highest accuracy of 97.26 % and outperformed the other three models along with the state-of-the-art models
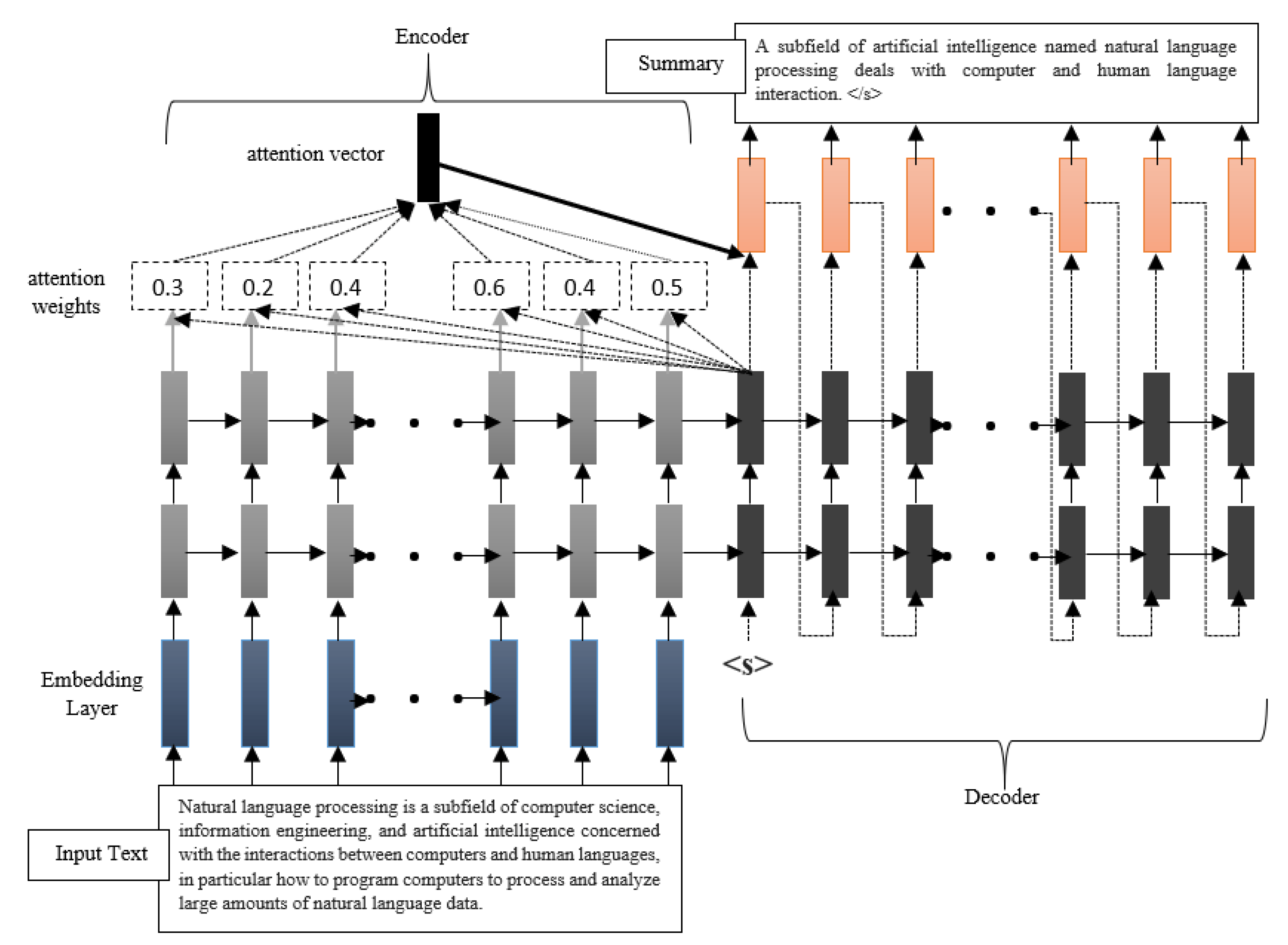
Summary: Abstractive text summarization that generates a summary by paraphrasing a
long text remains an open significant problem for natural language
processing. In this paper, we present an abstractive text summarization
model, multi-layered attentional peephole convolutional LSTM (long
short-term memory) (MAPCoL) that automatically generates a summary from a
long text. We optimize parameters of MAPCoL using central composite
design (CCD) in combination with the response surface methodology (RSM),
which gives the highest accuracy in terms of summary generation. We
record the accuracy of our model (MAPCoL) on a CNN/DailyMail dataset. We
perform a comparative analysis of the accuracy of MAPCoL with that of
the state-of-the-art models in different experimental settings. The
MAPCoL also outperforms the traditional LSTM-based models in respect of
semantic coherence in the output summary.